Table of Contents
What is Cloud Computing
Cloud computing is the on-demand delivery of IT resources over the Internet with pay-as-you-go pricing. Instead of buying, owning, and maintaining physical data centers and servers, you can access technology services, such as computing power, storage, and databases, on an as-needed basis from a cloud provider like Amazon Web Services (AWS).
In its simplest form, cloud computing provides an easy way to access servers, storage, databases, and a broad set of application services over the Internet.
Where we can use cloud
- File storage
- Big Data Analytics
- Data backups and archiving
- Disaster recovery
- Software testing and development
- Social Networking
- Infrastructure as a service (IaaS) and platform as a service (PaaS)
Features and benefits of cloud computing
- Instead of having to invest heavily in data centers and servers before knowing how you’re going to use them, you can pay only when you consume computing resources and pay only for how much you consume
- By using cloud computing, you can achieve a lower variable cost than you would get on your own
- With cloud computing, organizations can stop guessing about capacity requirements for the infrastructure necessary to meet their business needs
- In a cloud computing environment, new IT resources are one click away, which allows organizations to reduce the time it takes to make those resources available to developers from weeks to just minutes
- Cloud computing allows organizations to focus on their business priorities, instead of on the heavy lifting of racking, stacking, and powering servers
- Organizations can easily deploy their applications to multiple locations around the world with just a few clicks
Types of Cloud Deployment Model
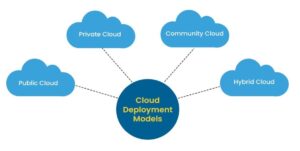
- Public Cloud
- The entire computing infra is located on the premises of the CSP
- Most economical option for those individuals/organizations that do not wish to invest in IT infrastructure.
- Private Cloud
- Its own Cloud Environment/Datacenters.
- The security and control level is highest while using a private network.
- Hybrid Cloud
- Combination Public Cloud and Private Cloud.
- It allows the sharing of data and applications between Public and Private Cloud environments.
- Organizations mainly use Hybrid Cloud when their On-Premise infrastructure needs more scalability
- Community Cloud
- Its shared by users of the same industry or by those who have common goals.
- This Cloud infrastructure is built after understanding the computing needs of a community as there are many factors including compliances and security policies which need to be included in the community Cloud infrastructure.
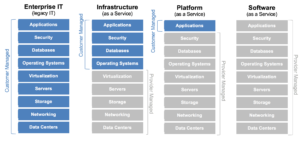
Types of Cloud Computing Services
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
- It provides a completely virtualized computing infrastructure that is provisioned and managed over the internet
- An IaaS provider manages the physical infrastructure (servers, data storage space, etc) in a data center, but allows customers to fully customize those virtualized resources to suit their specific needs.
- Ex: Microsoft Azure, Amazon Web Services (AWS), Cisco Metacloud, Google Compute Engine (GCE)
- Platform as a Service (PaaS)
- PaaS provides the framework needed to build, test, deploy, manage, and update software products.
- It utilizes the same basic infrastructure as IaaS, but it also includes the operating systems, middleware, development tools, and database management systems needed to create software applications.
- Most PaaS tools provide extensive pre-coded applications built into the platform, which can greatly reduce coding time and help companies get their products to market faster.
- Examples of PaaS: AWS Elastic Beanstalk, Apache Stratos, Google App Engine, Microsoft Azure
- Software as a Service (SaaS)
- SaaS is a fully-developed software solution ready for purchase and use over the internet on a subscription basis.
- The SaaS provider manages the infrastructure, operating systems, middleware, and data necessary to deliver the program, ensuring that the software is available whenever and wherever customers need it.
- Many SaaS applications run directly through web browsers, eliminating the need for downloads or installations.
- Examples of SaaS: Microsoft Office 365, Salesforce, Cisco WebEx, Google Apps.
- Function-as-a-Service (FaaS)
- Known as serverless computing
- FaaS allows customers to execute code responsively without having to allocate processing resources ahead of time.
- The cloud provider handles the infrastructure, allowing the customer to focus strictly on deploying application code.
- Customers only pay for the resources they use, making FaaS the truest form of “pay-as-you-go” cloud computing.
- Examples of FaaS: AWS Lambdas, Azure Functions.
Virtualization in Cloud model
- Virtualization allows to share a single physical instance of a resource or an application among multiple customers and organizations at one time.
- It does this by assigning a logical name to a physical storage and providing a pointer to that physical resource on demand
What is a hypervisor
- A hypervisor, also known as a virtual machine monitor or VMM, is software that creates and runs virtual machines (VMs).
- A hypervisor allows one host computer to support multiple guest VMs by virtually sharing its resources, such as memory and processing.
Hypervisor – Benefits
- Speed: Hypervisors allow virtual machines to be created instantly.
- Efficiency: Hypervisors that run several virtual machines on one physical machine’s resources also allow for more efficient utilization of one physical server
- Flexibility: Bare-metal hypervisors allow operating systems and their associated applications to run on a variety of hardware types because the hypervisor separates the OS from the underlying hardware, so the software no longer relies on specific hardware devices or drivers.
- Portability: Hypervisors allow multiple operating systems to reside on the same physical server (host machine).
Introduction of Cloud Computing