Table of Contents
Relational Database Service
- All relational DBs use Structured Query Language (SQL)
- Best suited for OLTP (On Line Transaction Processing)
- DBs are usually used in Enterprise applications/scenarios.
- Amazon Relational Database Service is a distributed relational database service by AWS.
- You can set up, operate, and scale a relational database in the AWS cloud.
- It provides cost-efficient and resizable capacity
- AWS will responsible to do hardware provisioning, database setup, patching and backups.
- You only focus on your applications so you can give them the fast performance, high availability, security and compatibility they need.
Infrastructure Management
- You are responsible for
- Managing DB Settings
- Building a relational DB schema
- DB performance tuning
- AWS is responsible for
- Security and patching of the DB instances
- Automated backups
- Software updates for the DB engine
- Multi-AZ with Synchronous replication between the active and standby DB instances
- Automatic failover if Multi-AZ option
- Providing the ability to create DB read replicas for DB read scaling
Supported Databases by AWS
- Supported DBs
- AWS Aurora
- PostgreSQL
- MariaDB
- MySQL
- MS SQL Server
- ORACLE
- Free Tier Details
- 12 MONTHS FREE
- 750 hours per month of db.t2.micro
- 20 GB of general purpose (SSD) database storage
- 20 GB of storage for database backups and database snapshots
RDS DB Instances
- A DB instance is a virtual machine with database environment running in the cloud.
- Can contain multiple user-created databases, accessed using the client tools and applications
- DB instances created and modified with
- AWS CLI
- Amazon RDS API operations
- AWS Management Console.
- Each DB instance has a DB instance identifier and it must be unique for that customer in an AWS Region
DB instance classes and storage
- The DB instance class determines the compute and memory capacity the instance
- DB instance class types
- Standard (balanced compute, memory, and networking)
- Ex: db.m3, db.m4, db.m5
- Memory Optimized (memory-intensive applications)
- Ex: db.r3, db.r5, db.x1
- Burstable Performance (burstable performance DB instance)
- Db.t2, db.t3, db.t4g
- Standard (balanced compute, memory, and networking)
- Amazon RDS storage types
- General Purpose SSD – offer cost-effective storage that is ideal for a broad range of workloads
- Provisioned IOPS – designed to meet the needs of I/O-intensive workloads
- Magnetic – low performance
RDS Backup
- Two types of backup for your RDS DB instances
- Automated backups
- Manual backups
Automated backups
- Amazon RDS creates and saves automated backups of your DB instance.
- RDS creates a storage volume snapshot of your DB instance, backing up the entire DB instance.
- Backups are stored in Amazon S3
- The first snapshot is a full one, and then subsequent snapshots are incremental
- Retention period: AWS RDS keeps the automated backup for 7 days by default
- Min 0 days (means no retention)
- Max 35 days
- RDS automatically backs up the DB instances daily, by creating a storage volume snapshot of your DB instance including the DB transaction logs
- You can choose the Backup Window time
- Enabled by default, you can disable it by setting retention period to zero
- Transaction logs are backed-up by RDS every 5 minutes
- Automated backups are used for point-in-time DB instance recovery
- It can restore the DB up to 5 minutes in time using the DB transaction logs and the automated snapshot
- During your daily backup window, your I/O may be suspended (for standalone RDS deployments)
- For Multi-AZ deployment, backups are taken from the standby DB instance
- Automated backups are deleted when you delete your RDS DB instance
Manual backups
- Manual snapshot not used for point-in-time recovery
- These snapshots stored in Amazon S3
- They are not deleted automatically when you delete your RDS instance. You have to manually delete from S3
- It is recommended to take a final snapshot before deleting your RDS DB instance
- Can be shared with other AWS accounts directly
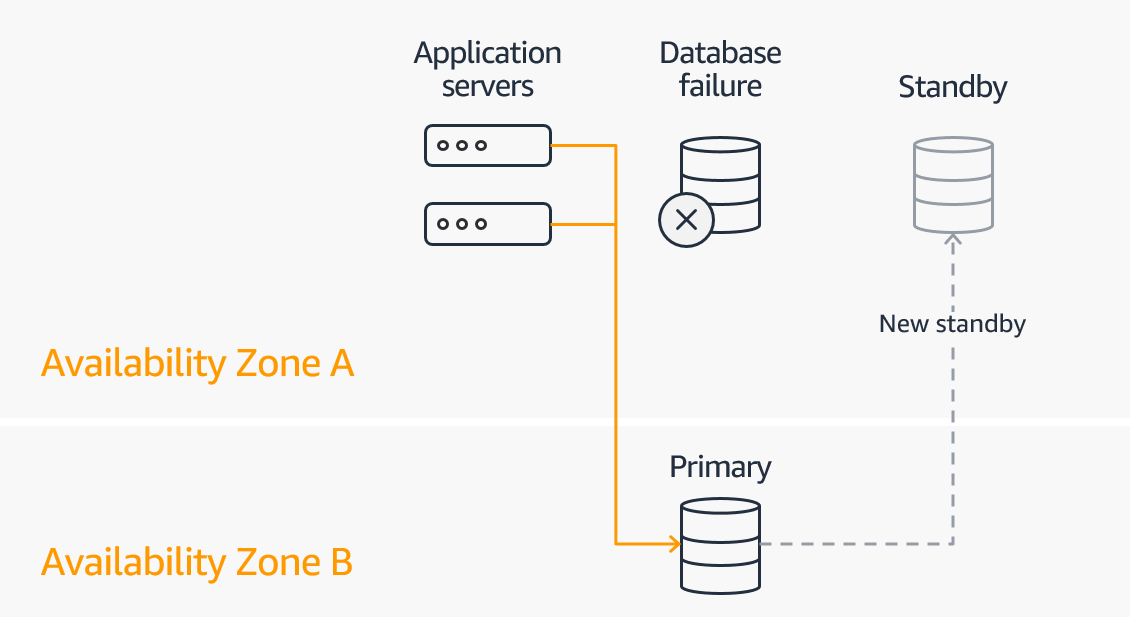
Amazon RDS Multi-AZ Deployments – Disaster Recovery
- Amazon RDS creates a primary DB Instance and synchronously replicates the data to a standby instance in a different Availability Zone
- Amazon RDS detects and automatically recovers from the most common failure scenarios for Multi-AZ deployments.
- Amazon RDS automatically performs a failover in the event of any of the following happens
- Loss of availability in primary Availability Zone
- Loss of network connectivity to primary
- Compute unit failure on primary
- Storage failure on primary
RDS Multi-AZ Deployments
- You can select the Multi-AZ option during RDS DB instance launch or modify an existing standalone RDS instance
- You can NOT read/write to the Standby RDS DB instance
- You will be alerted by a DB instance event when a failover occurs. AWS RDS uses AWS SNS to send RDS events via SNS notifications
- In Multi-AZ, snapshots and automated backups are done on Standby instance to avoid I/O suspension on Primary instance
- Maintenance sequence of events in Multi-AZ:
- Maintenance on Standby is performed
- Standby promoted to Primary
- Maintenance performed on old primary (Current Standby)
DB Read Replicas
- RDS Read Scalability
- A read replica is a replica of the primary RDS DB instance that can only be used for read operation
- Asynchronous replication. Reads are eventually consistent
- Read replicas are available in Amazon RDS for MySQL, MariaDB, PostgreSQL, Oracle, and SQL Server as well as Amazon Aurora
- Within AZ, Cross AZ or Cross Region
- Read replicas are used for SELECT
- not INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE
- Shifting read intensive applications such as Business reporting, or Data Warehousing to read from read replicas as opposed to overload the primary DB

RDS Read Replicas – Use Cases
- You have a production database that is taking on normal load
- You want to run some analytics on your data
- You create a Read Replica to run the new workload there
- The production application performance is unaffected
Amazon Aurora
- Aurora is a RDS from AWS (not open sourced)
- Aurora database build on top of Postgres and MySQL
- Aurora is AWS optimized and claims 5x performance improvement over MySQL and 3x over Postgres
- Aurora storage automatically grows in increments of 10GB, up to 64 TB.
- Aurora can have 15 replicas while MySQL has 5, and the replication process is faster
- Aurora costs more than RDS (20% more) – but is more efficient
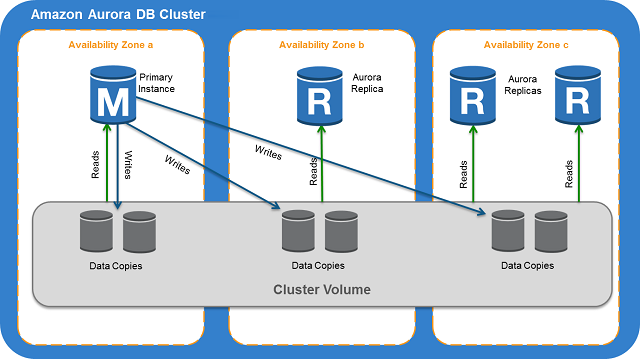
Amazon Aurora DB clusters
- An Aurora cluster volume is a virtual database storage volume that spans multiple AZs, with each Az having a copy of the DB cluster data.
- Primary DB instance
- Supports read and write operations. Each Aurora DB cluster has one primary DB instance.
- Aurora Replica
- Can have up to 15 Aurora Replicas.
- Maintain HA by locating Replicas in separate AZs.
- Automatically fails over to an Aurora Replica in case the primary DB instance becomes unavailable.
Features of Aurora
- Automatic fail-over
- Backup and Recovery
- Isolation and security
- Industry compliance
- Automated Patching with Zero Downtime
- Advanced Monitoring
- Routine Maintenance
- Backtrack: restore data at any point of time without using backups
Amazon RDS