Table of Contents
Content Delivery Network (CDN)
- A content delivery network (CDN) refers to a geographically distributed group of servers which work together to provide fast delivery of Internet content.
- A CDN allows for the quick transfer/loading of Internet content including HTML pages, javascript files, images, and videos.
- The CDN services continues to grow, and today the majority of web traffic is served through CDNs, including traffic from major sites like Facebook, Netflix, and Amazon
- Benefits of using a CDN
- Improving website load times
- Reducing bandwidth costs
- Increasing content availability and redundancy
- Improving website security
Popular CDN Services
- Cloudflare CDN
- Akamai CDN
- Amazon CloudFront
- Microsoft Azure CDN
- Google Cloud CDN
- Alibaba Cloud CDN
- Imperva Cloud Application Security
- Rackspace CDN
- Fastly CDN
- CDN77 CDN
What is AWS CloudFront
- Amazon CloudFront is a fast content delivery network (CDN) service that securely delivers data, videos, applications, and APIs to customers globally with low latency, high transfer speeds, all within a developer-friendly environment.
- Use cases
- Deliver fast, secure websites
- Accelerate dynamic content delivery and APIs
- Stream live and on-demand video
- Distribute patches and updates
AWS CloudFront
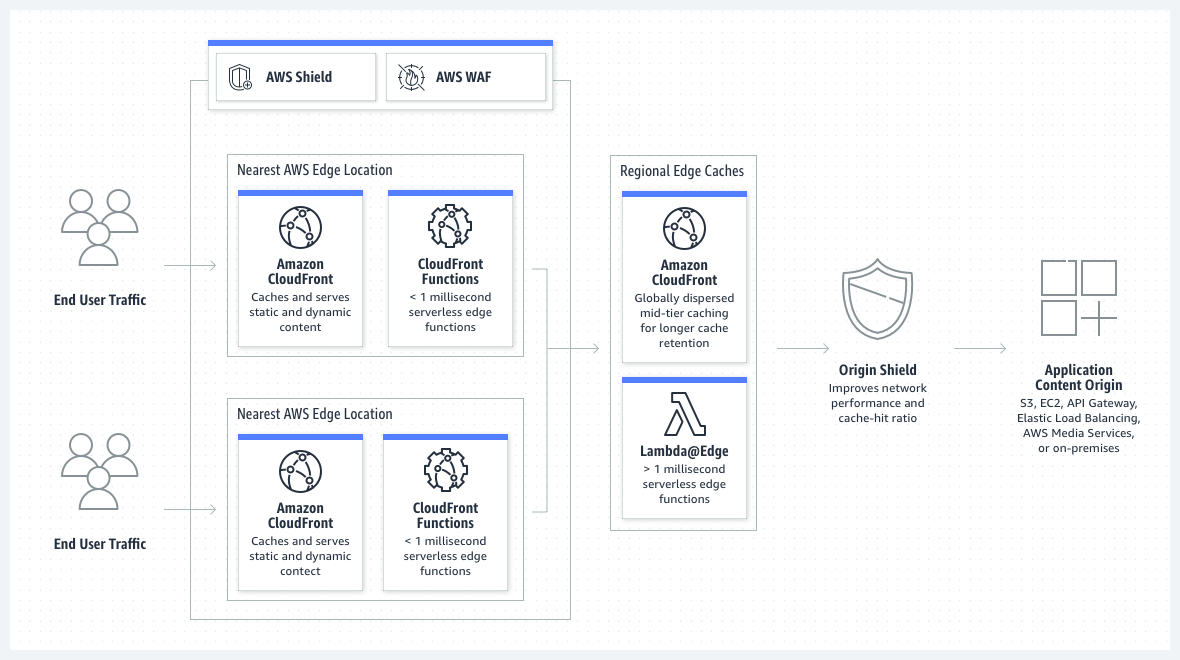
- CloudFront is a global (not regional) service.
- Amazon CloudFront is a web service that speeds up distribution of your static and dynamic web content, such as .html, .css, .js, and image and video files.
- CloudFront delivers your content through a network of data centers called Edge Locations.
- When a user requests content that you’re serving with CloudFront, the user is routed to the edge location that provides the lowest latency.
- Amazon CloudFront has added several regional edge cache locations globally.
- DDoS protection, integration with Shield, AWS Web Application Firewall
CloudFront Origins
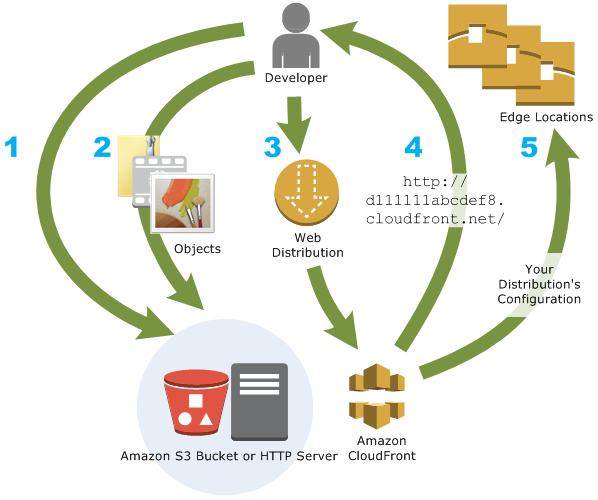
- An origin is the location where you store the original web content, which you want to distribute via CloudFront
- S3 bucket
- For distributing files and caching them at the edge
- Enhanced security with CloudFront Origin Access Identity (OAI)
- Custom Origin (HTTP)
- Application Load Balancer
- EC2 instance
- S3 website (must first enable the bucket as a static S3 website)
- Any HTTP backend you want

Amazon CloudFront Distributions
- Web Distributions: serve the following content over HTTP or HTTPS:
- Static and dynamic download content, for example, .html, .css, .js, and image files, using HTTP or HTTPS.
- Multimedia content on demand using progressive download and Apple HTTP Live Streaming (HLS).
- Your origin can be either an Amazon S3 bucket or an HTTP server
- RTMP distributions
- Stream media files using Adobe Media Server and the Adobe Real-Time Messaging Protocol (RTMP).
- An RTMP distribution must use an Amazon S3 bucket as the origin.
- CloudFront lets you create a total of up to 200 web distributions and 100 RTMP distributions for an AWS account.
CloudFront Invalidation
- If you need to remove/update an object from CloudFront edge caches before it expires, you can do one of the following:
- Invalidate the object from edge caches. The next time a viewer requests the object, CloudFront returns to the origin to fetch the latest version of the object.
- Use object versioning to serve a different version of the object that has a different name.
- You can’t cancel an invalidation after you submit it.
- You can invalidate most types of objects that are served by a web distribution
- You cannot invalidate media files in the Microsoft Smooth Streaming format when you have enabled Smooth Streaming for the corresponding cache behavior.
Geographic Restrictions
- You can use geo restriction, also known as geo-blocking, to prevent users in specific geographic locations from accessing content that you’re distributing through a CloudFront web distribution.
- Restriction type
- No restrictions
- Allow list
- Block list
Amazon CloudFront